What is INP in Core Web Vitals?
In the realm of web development, understanding the intricacies of Core Web Vitals is paramount, and within this framework, “Input Timing” (INP) stands as a crucial metric. INP in Core Web Vitals encapsulates the responsiveness of a website during user interactions, scrutinizing delays and layout shifts. Consisting of First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), INP delves into the time lapse between user actions and a site’s response. This introduction sets the foundation for a comprehensive exploration of INP, unraveling its components, impact on user experience, optimization techniques, and its broader implications for website performance and search engine rankings.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Core Web Vitals:
In the dynamic landscape of web development, understanding INP in Core Web Vitals is integral. Core Web Vitals gauge a website’s user experience, with Input Timing (INP) serving as a pivotal metric. INP scrutinizes delays and layout shifts during user interactions, encompassing First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). This introduction lays the groundwork for an in-depth exploration of INP’s components, its impact on user experience, effective optimization strategies, and the broader implications for a website’s performance and search engine rankings. In the evolving digital realm, mastering Core Web Vitals, especially INP, is key to crafting seamless and user-friendly online experiences.
What Does “Inp” Stand For?
INP in Core Web Vitals refers to “Input Timing,” a pivotal metric measuring a website’s responsiveness to user interactions. The term “Inp” encompasses two critical components: First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). FID assesses the delay between a user’s first interaction and the site’s response, while CLS evaluates unexpected layout shifts during interactions. Understanding “Inp” is essential for web developers and SEO professionals, as it directly influences user experience and search rankings. Mastering the intricacies of Input Timing aids in optimizing websites for seamless interactions, ensuring a positive and engaging online experience for visitors.
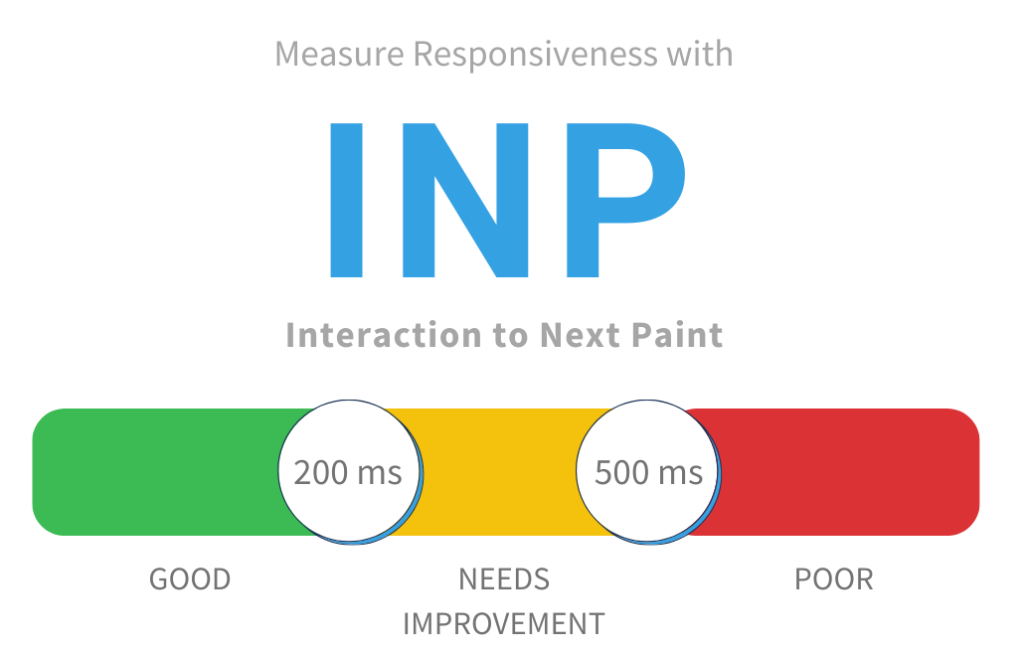
Inp Components:
Exploring the realm of INP in Core Web Vitals, it’s crucial to dissect its components. “Input Timing” comprises two fundamental elements: First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). FID measures the delay between a user’s initial interaction and the website’s response, assessing responsiveness. On the other hand, CLS evaluates unexpected layout shifts during user interactions, gauging the visual stability of a page. Recognizing and optimizing these INP components are essential for developers and site owners aiming to enhance user experience and navigate the intricate landscape of web performance, aligning their websites with the evolving standards of Core Web Vitals.
First Input Delay (FID):
INP in Core Web Vitals introduces a critical component: First Input Delay (FID). FID measures the delay between a user’s initial interaction, such as clicking a button, and the website’s response. A low FID is crucial for a positive user experience, indicating a site’s responsiveness. Long delays can lead to frustration. Developers and site owners focus on optimizing FID by minimizing script execution times and leveraging browser optimizations. Understanding FID within the broader context of Core Web Vitals helps in crafting websites that not only captivate visitors with engaging content but also ensure a smooth and responsive interaction, contributing to overall user satisfaction.

Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS):
INP in Core Web Vitals encompasses Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), a vital metric gauging a website’s visual stability during user interactions. CLS evaluates unexpected layout shifts, such as elements moving unexpectedly on the page. A low CLS score is crucial for providing a seamless user experience, preventing jarring shifts that may lead to confusion or frustration. Developers focus on optimizing CLS by ensuring proper element sizing, avoiding late-loading images, and employing other best practices. Understanding CLS within the broader context of Core Web Vitals aids in crafting websites that prioritize not just content but also a visually stable and enjoyable user interface.
Inp Measurement Tools:
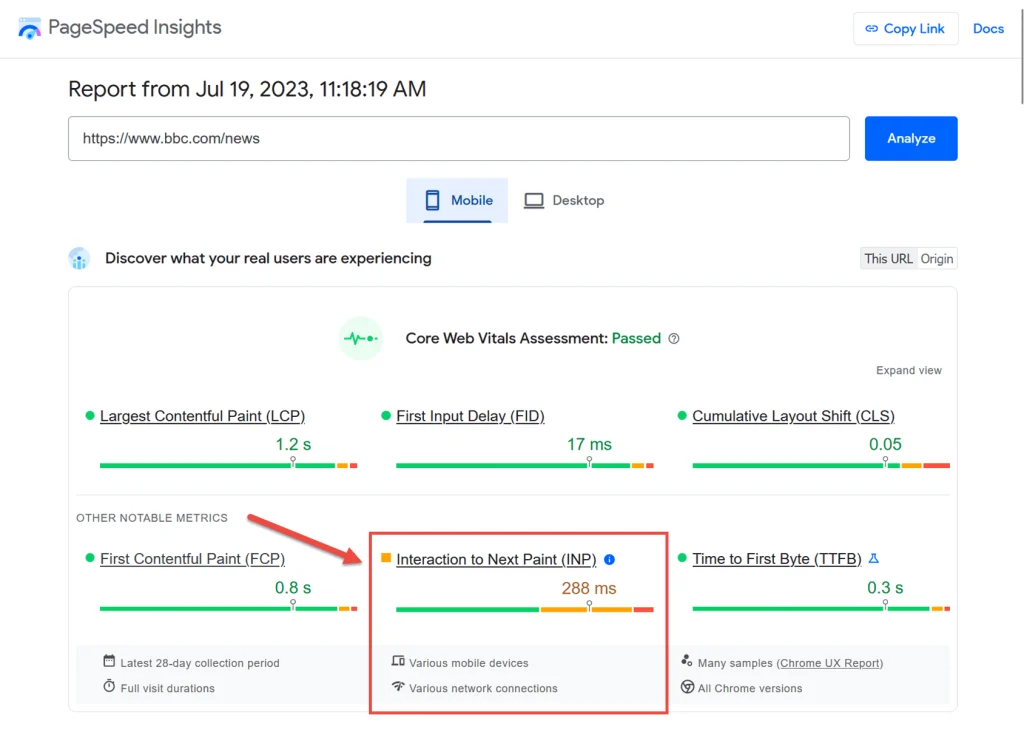
Navigating the landscape of INP in Core Web Vitals involves utilizing specialized measurement tools. These tools are essential for quantifying and optimizing the Input Timing metric, ensuring a responsive website. Platforms like Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and other web performance tools offer insights into First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Developers leverage these tools to identify areas for improvement, analyze performance metrics, and implement optimizations that enhance user interactions. With the aid of these measurement tools, web professionals can fine-tune the responsiveness of their websites, aligning them with the evolving standards of Core Web Vitals.
Impact of Inp on User Experience:
The impact of INP in Core Web Vitals on user experience is profound. Input Timing directly influences how users perceive and interact with a website. A low First Input Delay (FID) ensures quick responsiveness, creating a smooth and engaging browsing experience. On the other hand, a high FID can lead to frustration and a perception of sluggishness. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) influences visual stability, preventing unexpected layout shifts that can disrupt users. A low CLS score contributes to a visually cohesive experience. By optimizing INP components, developers enhance user satisfaction, retention, and overall perception of a website’s performance.
Optimizing for Inp:
Optimizing for INP in Core Web Vitals is pivotal for ensuring a responsive and user-friendly website. Developers focus on reducing First Input Delay (FID) by optimizing scripts, minimizing unnecessary third-party code, and leveraging browser caching. For Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), proper image and video element sizing, utilizing CSS for dimensions, and loading resources with appropriate aspect ratios are key. Employing asynchronous loading for non-essential scripts also aids in reducing FID. Prioritizing these optimizations not only aligns the website with Core Web Vitals standards but also enhances overall user satisfaction by providing a seamless and visually stable browsing experience.
Monitoring and Improving Inp Scores:
Constantly monitoring and improving INP in Core Web Vitals scores is integral for maintaining an optimal user experience. Web developers employ tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse to regularly assess First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). By identifying areas of concern and understanding the factors influencing INP, developers can implement targeted optimizations. This iterative process involves refining scripts, addressing layout shift issues, and continually fine-tuning website performance. Regularly monitoring and improving INP scores ensures a website remains responsive and visually stable, meeting the evolving standards of Core Web Vitals for an enhanced and consistent user experience.

Inp and SEO:
The relationship between INP in Core Web Vitals and SEO is significant. Google considers user experience metrics, including Input Timing, as ranking factors. A website with low First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) scores is more likely to rank higher in search results. Google’s emphasis on Core Web Vitals highlights the importance of a smooth, responsive, and visually stable user experience. Optimizing for INP not only enhances user satisfaction but also contributes to improved search engine rankings, underscoring the interconnected nature of website performance, user experience, and overall visibility in search engine results.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, INP in Core Web Vitals plays a pivotal role in shaping a website’s performance and user experience. Understanding and optimizing First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) are crucial for meeting the evolving standards of web development. Constant monitoring, fine-tuning, and leveraging measurement tools ensure a responsive, visually stable, and SEO-friendly website. By prioritizing these aspects, developers enhance user satisfaction, positively impact search engine rankings, and create an online environment that aligns with the dynamic expectations of both users and search engines. INP, within the broader framework of Core Web Vitals, becomes a cornerstone for crafting successful and impactful websites.
Read More What are the Benefits of SEO Company?
FAQ’S
What is First Input Delay (FID) in Core Web Vitals?
FID measures the delay between a user’s first interaction on a website and the site’s response, crucial for assessing responsiveness.
How does Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) impact user experience?
CLS evaluates unexpected layout shifts during interactions, influencing visual stability and user perception on a webpage.
Why is optimizing for INP important for SEO?
Google considers user experience metrics, including INP, as ranking factors, making optimization essential for improved search engine rankings.